
One of the very first ways to get traffic on the Internet was ranking in the search engines, and this has never been truer today. While the strategies and tactics to rank on Google have vastly changed in the last two decades, the end result for quality SEO and authoritative websites has always been the same:
Give your visitor the best possible ability to find useful information on your website.
Most people think of SEO as ranking better on the search engines, particularly Google. However, when delving into your SEO strategy, don’t think of it this way. Think of it as an all-encompassing strategy of allowing organic traffic to flow as easily as possible through your website, along with high quality content that your visitor finds useful.
Remember, Google can only exist and make money if the user is satisfied with the results in a search. If enough people search for something and don’t find adequate information or content that answers their search, they will turn to a competitor.
Here are the top seven ranking factors that are vitally important to rank on Google in 2021 and beyond.
1. Links and Links (But Quality Links)

Originally, it was all about links. Each time another website linked to you, it was considered a vote of confidence, and you were pushed higher in the rankings. This is how Google became the dominant engine in search.
The thinking went that if one website owner is referring to another website by linking to it, then that owner must trust it and think of it as worthy information to share … aww, those innocent days of 1999!
Links are still vitally important today, but what has changed through the years are the types of websites, the words in the links, and the kind of links that a website has … basically, the quality of who links to you, and how they do it. If you have a tech blog, one link from Apple is worth a thousand links from smaller, less authoritative websites.
Make sure you download our comprehensive 55+-page guide so that you get an in-depth look at search engine optimization strategies for 2021. Click the button below to get it now!
2. Your Content (Which is King)

Early on, Google made a lot of effort to distinguish good content from bad content. Repeating keyword stuffing, invisible text and other spam techniques are obvious, but more difficult is measuring the quality of the content.
In 20 years, Google has become extremely good at this, with several algorithms and millions of dollars devoted to language processing and semantic theory.
Today, instead of just looking at individual keywords on a page, they now look at the overall document, the relevancy of the search query and user intent (which I will discuss below.)
The end result is that your page must be as informative and high quality as you can make it. Remember, Google wants the user to find the best and most satisfying result to answer their search query.
3. Page Experience

This is a newer ranking factor in Google, and encompasses nearly everything that is on your page and that you can control. It’s also known as “on page” ranking factors, because it’s everything to do with the page that your viewers will see.
This will get a bit technical, but I will break everything down for you.
Core Web Vitals
If you do a search for “core web vitals”, you’ll see a scary technical image like this:
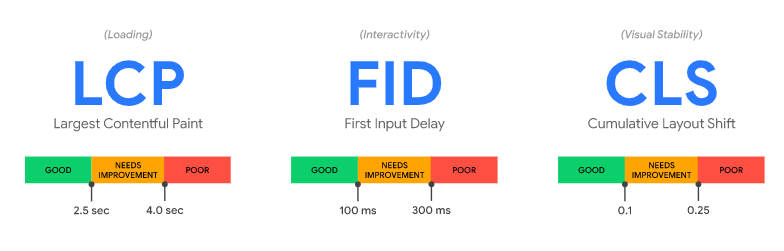
Don’t worry! Google is simply measuring your website speed and response when visitors visit your site. They have placed priority on website speed for a few years now, due to a majority of searches now coming through mobile.
Through lots of research and anonymous data collection throughout the years (mainly through the Chrome browser), Google engineers know that people begin to get impatient if the page they search is still loading after even one second.
This makes sense. You are busy standing on a street corner, wanting to know the closest pizzeria … you want the results NOW.
In previous years, Google mentioned technical factors, such as speed, bounce rate, the layout of your website, etc. However, the messages and signals were all separate and haphazardly mentioned and organized.
With Core Web Vitals, Google is trying to make things simpler. They are unifying all technical factors into one main measurement with one tool, which is available in your Google Search Console.
Here’s an example of a detected problem on one of my websites:
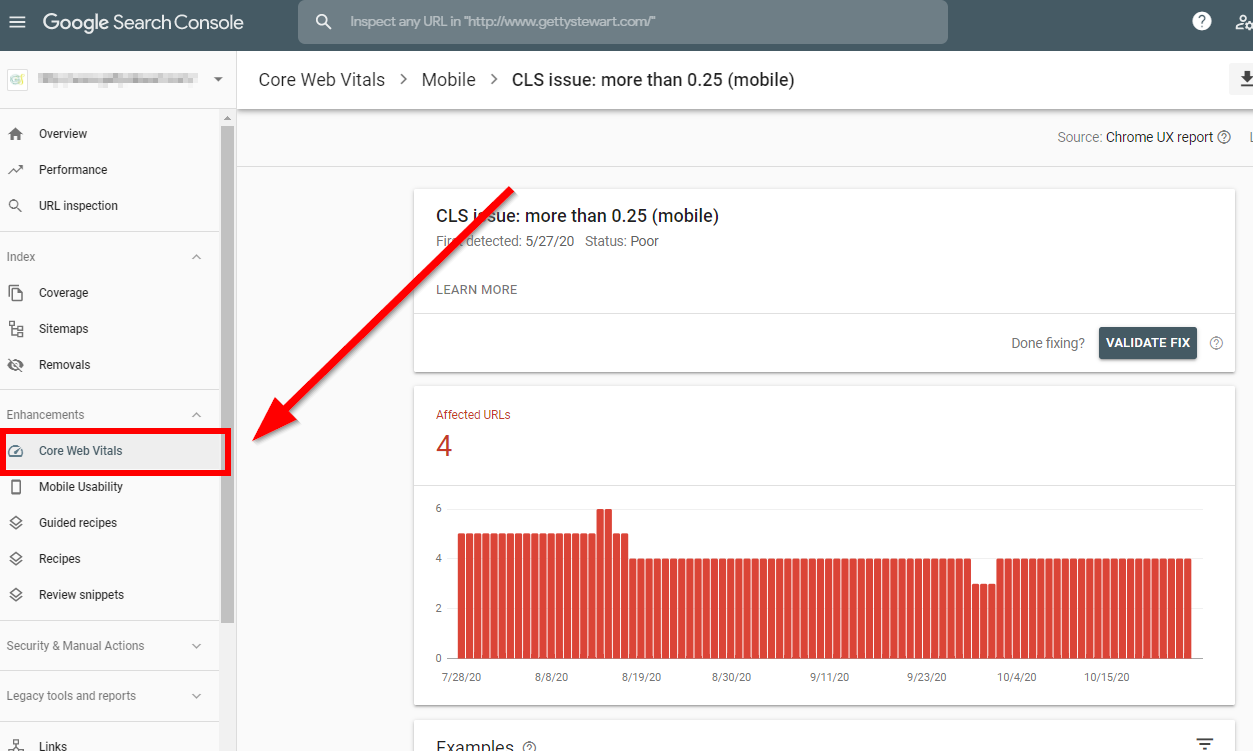
Google is trying to make it as easy as possible to explain how to fix errors that could be holding some of your pages back and creating a poor user experience. If you have some weird errors in your Core Web Vitals report, there will be in-depth explanations for them.
For 2021 and beyond, they are focusing on three of these technical factors:
LCP – Largest Contentful Paint
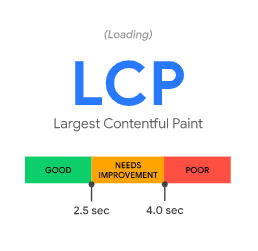
Basically, it’s the loading time of your page. More specifically, it’s the time it takes for the largest element on your page to load (thus the word “Largest” in the title).
Anything under 2.5 seconds is good. If it’s 4 seconds it will need improvement, and if it takes over 6 seconds it’s considered poor.
To find out the speed of your website, go to PageSpeed Insights or GTmetrix to see how fast your webpage loads.
This is my score in GTmetrix when the WordPress speed plugin is disabled:
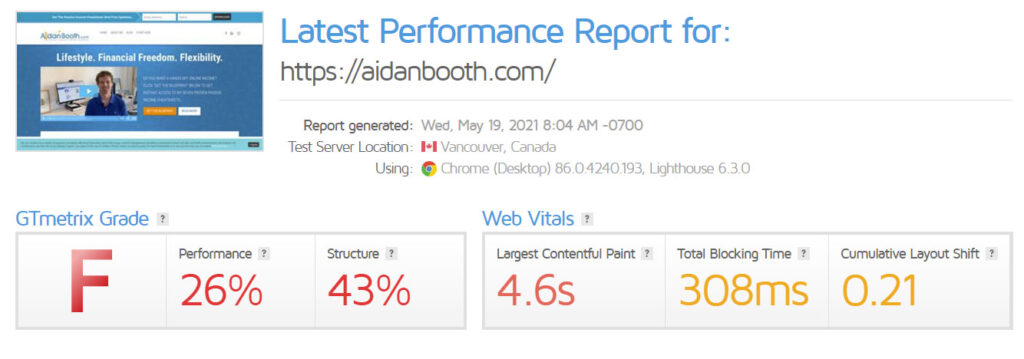
And this is what happens when I active it:
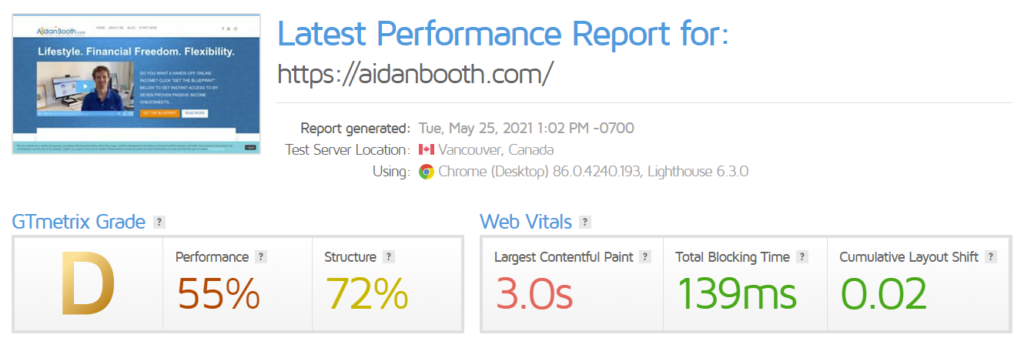
My website is still quite slow and can use further improvements, and it is a project I have in the pipeline. However, using a plugin to increase speed can make all the difference. Shaving off 1.6 seconds, while it doesn’t seem like much, doubled the performance rating.
Here are some things you can do to speed up your website:
- If using WordPress, install what is called a caching plugin, such as W3 Total Cache or WP Super Cache. They are free and help compress and speed up your website pages.
- Making images smaller (for WordPress, you can use an image reduction plugin called WP Smush that will automatically reduce image sizes when you upload them)
- Remove any unnecessary plugins from your WordPress website (each plugin adds a bit more load time)
- Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN) which caches your website on a global network of servers. Normally, if your website is on a web host in England, and an Australian visitor clicks to your website, the information will be retrieved from England. With a CDN, a quick, stored copy of your website will be retrieved from the closest CDN, which is hopefully in Australia.
- Store videos and other large media files off your website. Instead of having visitors retrieve a video from your website, place it on YouTube and embed the YouTube code onto your webpage.
- Move to a new web host. If you’ve done everything you can to fix your website, and it is still slow, it could be your web server. Maybe your web host package is too cheap and limits the speed. Or it is unreliable with old computer servers. It could be time to switch to a better host.
I talk more extensively about Google’s Core Web Vitals. Access the 55+ report on SEO strategies completely for free by clicking the button below!
FID – First Input Delay
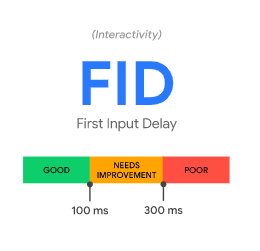
Did you ever feel frustrated when you click a link on a website, only for it to take an entire second for that click to respond?
Or you click to scroll down, and nothing responds … then it finally does?
FID is the amount of time it takes from when a user first interacts with your page (clicking or pressing a link, for instance) to when the page responds. Fortunately, this factor is related to the speed and response time of your website. Everything you do to increase your LCP will help your FID.
The response to that click (for instance, loading to a new page) should be 0.1 second, or 100 ms. Anything more than 300 ms is poor.
CLS – Cumulative Layout Shift
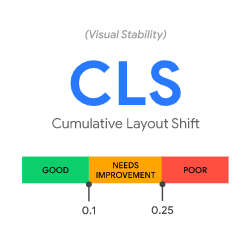
Have you ever started reading something online when suddenly the text jumps down the page because an ad has loaded above it?
This would be an example of poor CLS. The reason this happens is because ads, images, video or scripts are still loading on the page after the text appears.
The CLS is a score between 0 (no shifts) and 1 (everything shifts after the page is loaded.) A good score is 0.1 … or only 10% or less of all elements on your page are still unstable and will potentially shift after it is presented to you.
So, the next question is, how to improve this score?
- Specify the dimensions in images and videos. The images will scale based on screen size, as modern browsers take these initial dimensions to set the actual size.
- Specify the dimensions in ad placements. Most ads are dynamic, in that they will resize based on the size of the screen. To avoid layout shifts, explicitly define the height and width in the ad container. Find out from your ad provider what the usual sizes are for what you are displaying.
- Use common web fonts. Often a browser will substitute a fallback font to the viewer until your custom font finishes loading. If you are using Google fonts, make sure to use the “preload” tag in the code.
WordPress optimization plugins that fix website speed will also help, as they will consolidate scripts into optimized files to reduce the size and time to load, avoiding your page jumping around when visible to the viewer.
4. Ready to E.A.T.?

Another recent Google update has to do with quality information. It’s not one single part of the ranking algorithm, but a multitude of signals to determine quality to fight against misinformation and deceptive content.
E.A.T. stands for:
- Expertise
- Authority
- Trustworthiness
Google has thousands of human quality raters who do nothing but review webpages. They are provided with quality research guidelines that mention this E.A.T. factor well over a hundred times.
These standards are mainly concerned with medical and financial websites … any type of niche where the choices visitors make due to your content can affect them in a life-changing way.
Because of this, Google often calls them “Your Money or Your Life”-type niches and websites, and pay particular attention to them.
Here’s some examples of these types of niches:
- Health and wellness
- Finance and financial advice
- Law and civil rights
- News websites (politics, business, science, technology, etc … but not necessarily sports and entertainment.)
For example, when searching about making investments, Google wants to ensure you are getting advice from an expert on the subject. The last thing Google wants is to serve people incorrect or fraudulent information!
5. User Intent

Another important ranking factor in 2021 is the concept of user intent. Basically, what is the user looking for?
This sounds simple in concept, but let’s give an example. Say you type in “apple” … what exactly is your intent for this search?
- Are you looking for Apple, the company?
- Are you looking for the fruit?
According to Google, your intent is to search for Apple, the tech company, not the fruit:
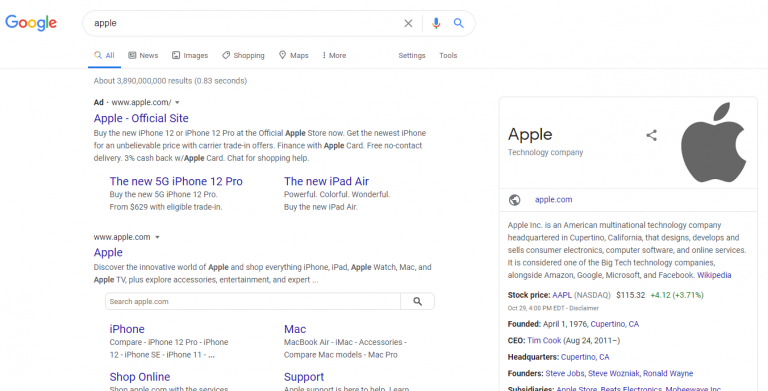
When you type in “apple”, how does Google know that it is, indeed, the tech company you are looking for? That’s the multiple-million dollar question that has involved years of semantic research, linguistic theory, and artificial intelligence programming.
What does this mean for you, as the owner of a website trying to perform SEO? It means matching your content with the proper search intent for the keyword phrase you wish to rank for.
Let’s give another example: “SEO strategy” … if you wished to rank for this keyword term, what content would you write about, and how would you present it? There are several options, some of which would be WRONG:
What is the user intent for the query “SEO strategy?”
- A list of case-studies on companies with a successful SEO strategy
- A list of tips for your SEO strategy
- A template and/or steps to creating an effective SEO strategy
And the correct user intent is (drum roll) …
#3: A template and/or steps to creating an effective SEO strategy
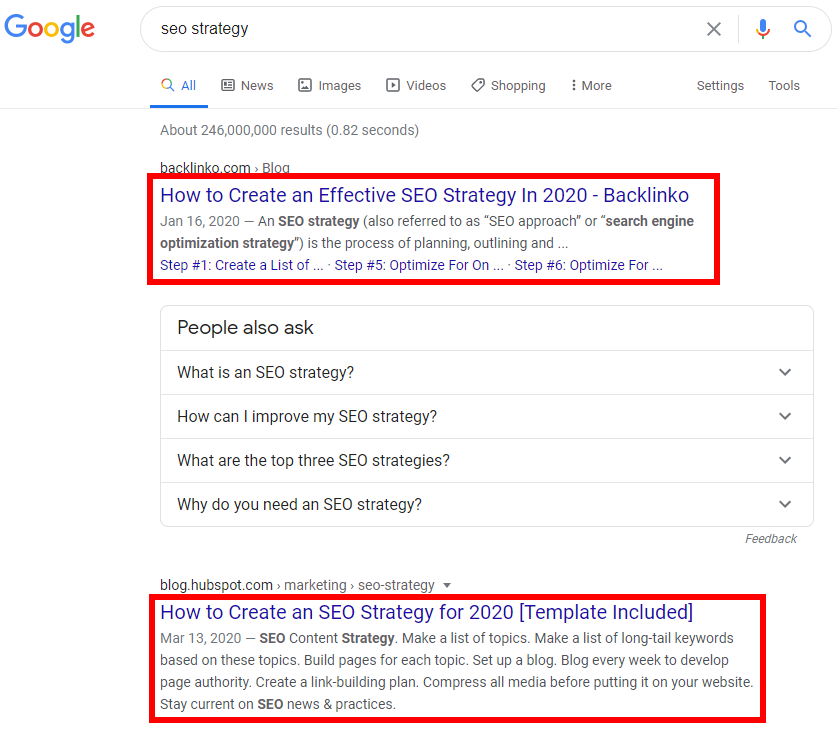
Knowing the user / search intent of a keyword phrase you wish to rank for is vital to ranking your page. Without knowing the intent, you could spend hours and vital resources writing about case studies of successful SEO strategies, or just a large list of SEO tips … excellent content for sure, but you would never be able to rank on page 1 for “SEO strategy”.
Google categorizes three types of user intent:
- Informational intent – “How to make pizza.”
- Navigational intent – “pizza near me.”
- Transactional intent – “order pizza.”
Informational Intent (“Know”)
This type of search query is for people looking for information and answers to questions. It would usually be a specific question on how to do something or know something. This is the main form of intent Google focuses on, because there are so many multiple interpretations of the same question.
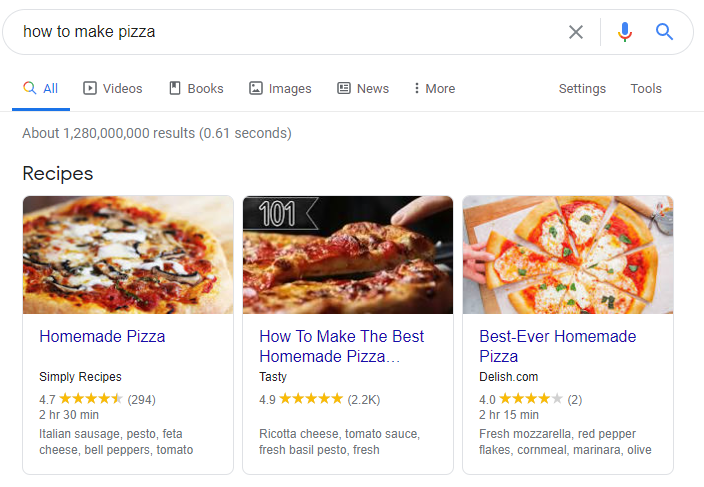
Navigational Intent (“Where”)
These would be location queries. In fact, just by typing in “pizza”, Google knows your intent is to find a local pizza place. It’s not to find out the history of pizza or how to cook the best pizza.
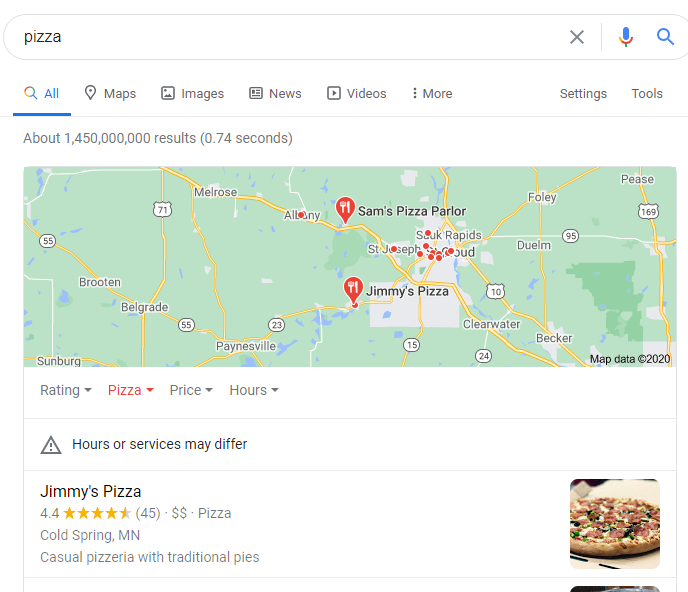
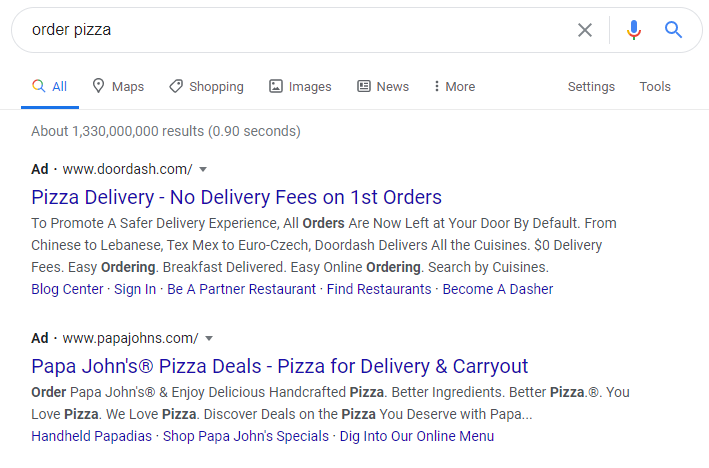
Transactional Intent (“Do”)
The user is ready to complete some sort of action. This is likely to buy a product, sign up for an email, or pick up the phone for something. Most likely, Google will first display ads.
How to Research User Intent
Now that you know what user and search intent is, you can be aware of this while researching and writing content that you wish to rank.
When doing your research, make sure to do actual search queries for your keyword phrases to see what Google says is the intent. It could be different from what you were planning to write about.
As well, view Google’s “Searches related to” results, as these are closely related to the intent. Back to the “SEO strategy” example, you would further realize that the best answer and intent is for a strategy plan and template.

6. Voice Search

Google is actively evolving voice search from simply “recognizing” search patterns to “understanding” spoken queries. The biggest take-away is that the spoken language is very different from the written language (ask any student studying English as a second language!)
Usually, a typed-in search is shorthand, such as “weather New York”. For voice search queries, it is usually the entire sentence. “Hey Google, what is the weather like in New York?”
You also have to think about the current behavior of a written versus a voice search. Somebody who types in a search is likely doing research, while a voice query is more likely a visitor who wants instant results right now. Your content needs to appeal to both type of visitors.
When somebody does a voice search on their phone to Google, what does the voice assistant return? For instance, let’s imagine this query:
“OK Google, what is the best time to post on Instagram?”
Spoken on a mobile phone or a screenless device like Google Home, the assistant will speak through a Google search result (and say the website name or brand it comes from), but which one?
Most likely, it will read “Position 0”, or the featured snippet:
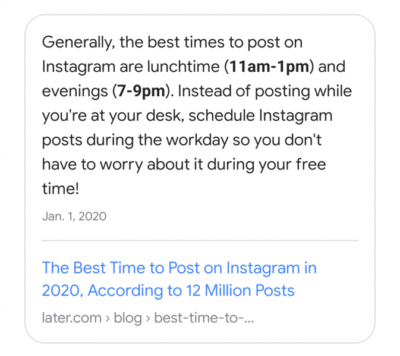
So, how did this post get the featured snippet and therefore the voice search result? I have an entire PDF you can download with a large section on how voice search works. Simply click on the button below for instant access!
7. Video Marketing

My final top strategy for SEO in 2021 and beyond is video marketing. Google first introduced video carousels to the rankings in 2018, and since then they have only gained in prominence.
Though not a ranking factor, video is quickly becoming what visitors prefer with their content. The truth is, as we all enter beyond 2021, video content is only becoming more and more important. Check out my guide to producing video like a pro for more info.
Types of Videos
Here are some types of videos to incorporate into your content and marketing:
How-To Videos

This is one of the most popular types of video content. People search for guides on how to use or repair a product. It could be about anything – phones, software, apps, cars, washing machines, etc.
Marketers gain subscribers and can create an extra income stream when they post tutorials that help people save time and money and teach them how to do something.
Unboxing or Product Demo

An unboxing video is exactly what it sounds like: You receive a package from a company and film yourself taking it out of the box and packaging, putting it together and testing it.
This is great if you have an affiliate or ecom website. If you have a brand, you would of course have demos of your products or services. As a bonus, ask a third party or social influencer to review or demo your product instead. Viewers and followers trust these more.
Testimonials and Reviews

You yourself don’t have to face the camera. Let your customers do the talking instead. They can speak about you, your product, brand or service, and their (positive) experiences with your business.
Since testimonials are a form of 3rd-party endorsements, your audience will trust and believe them more than a video advertisement.
For reviews, “Top 10” of something are great formats for video. Simply have a slideshow of the top 10 products in the niche you are in, and talk about them (or hire somebody to do this for you.)
Publishing Platforms for Video
Without a doubt, YouTube would be the place to publish your videos.
It’s the second most popular social network, and second largest search engine. It’s also owned by Google, so you can imagine how seriously Google takes video and incorporates it into search.
You can upload videos on YouTube seconds after creating an account. Then take that video and embed it into your website page. For a WordPress site, all you need is to copy and paste the code.
You can also publish video on Facebook, Instagram, Snapchat and TikTok, depending on your social media marketing strategy.
There you have it, the 7 top ranking factors in Google in 2021 and beyond. One common theme throughout this article has been a people-first strategy. This has been Google’s goal since its inception in the late 1990’s, and it is only becoming more and more important as search engines and the Internet evolves.
What are your thoughts about Google’s 2021 updates? Have you seen an increase or decrease in your traffic? What do you need to do to improve your core web vitals and succeed in Google to rank well past 2021? Please comment below.






Just started dipping my toes into content marketing and SEO itself. On an information overload, but your free guide is one of the easy ones to follow. thanks!
Woah, SEO never slows down! Thanks for the post, Aidan. I really liked the info on user intent. I’ll have to check my site to make sure everything is up to date.
There’s always something new happening in SEO world!
Been a long time since I dabbled in SEO. Back then it was just links and keywords, and then more links. Definitely got a lot to catch up on. Would definitely be reading more about core web vitals, thanks to you!
It’s worth delving in to David, a lot of quality traffic to be found!
Tried GTmetrix on my site just now and got an F too. Yikes. Been wondering why my site was so slow and now I know. Apprciate the tips, and hopefully this raises my page grade too!
Let us know how you get on with your site optimization!
I read somewhere last year that videos would be the next big thing in content – and they were right! Literally on every platform now.
Thanks for this nice read.
Yup, video is here to stay!
Were you aware that your “Foundational SEO” button in this post
pops a signup form, but the “send me the guide” button doesn’t actually work?
Not on Firefox anyway 🙂
That’s odd Joe.. will look into it. Thanks
Download not working on google chrone/android
Hmm, I can’t seem to replicate the issue.. please contact my support desk and we’ll send you the file manually: http://support.blueprintcentral.com